For patients with chronic lower back pain (CLBP)
Power Comes From Within
The RelieVRx® program is the first FDA-authorized in-home virtual reality (VR) treatment clinically proven to deliver significant, lasting reduction of chronic lower back pain.1-3
SEE THE PROOF
The RelieVRx program uses a non-pharmacologic, non-invasive medical device designed to help patients manage their CLBP2
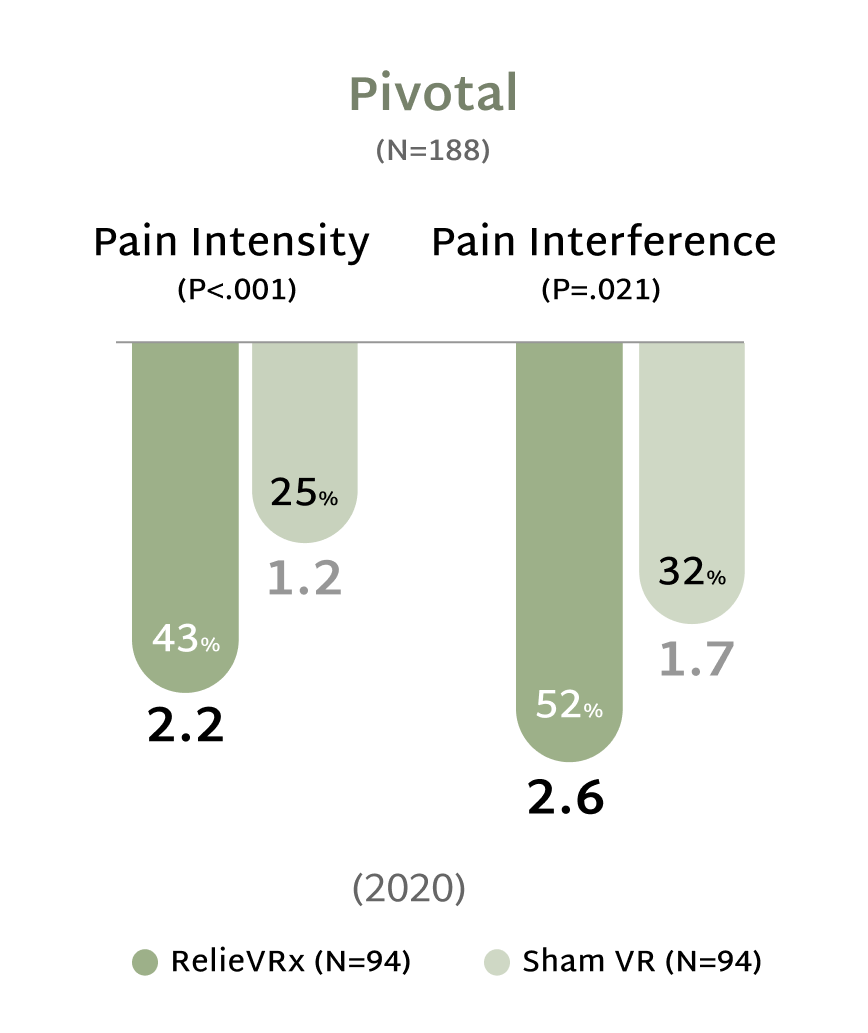
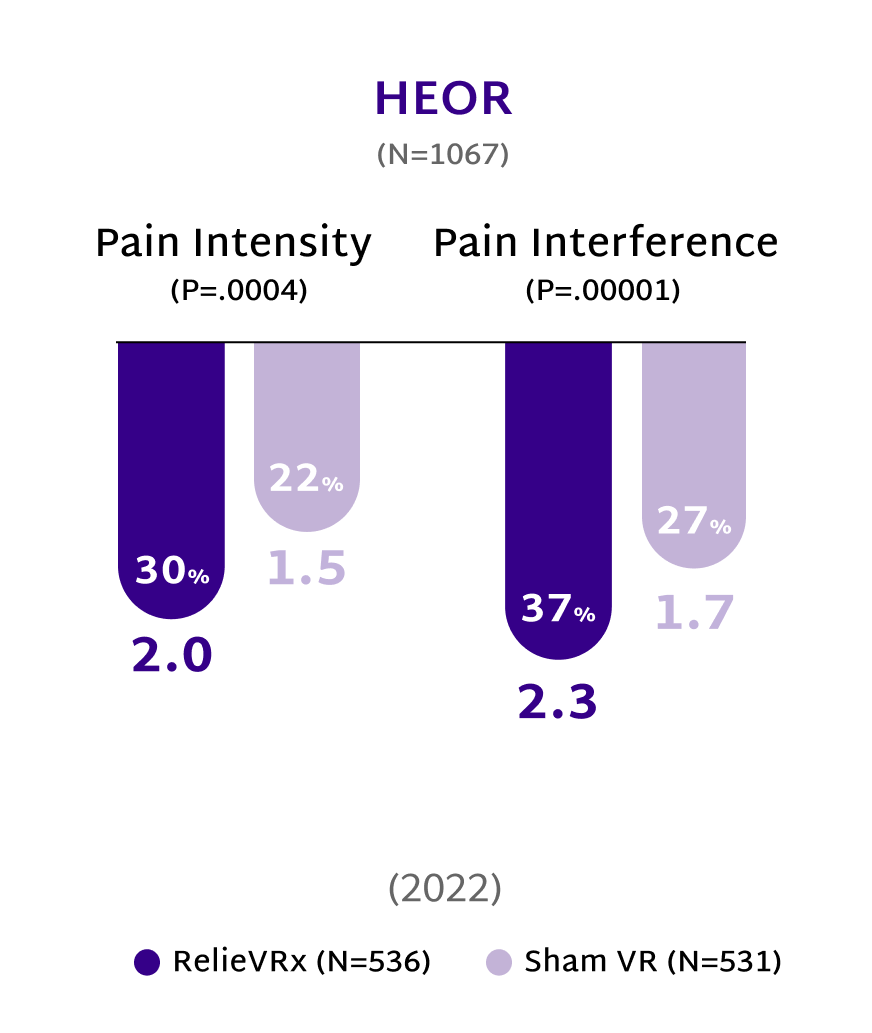
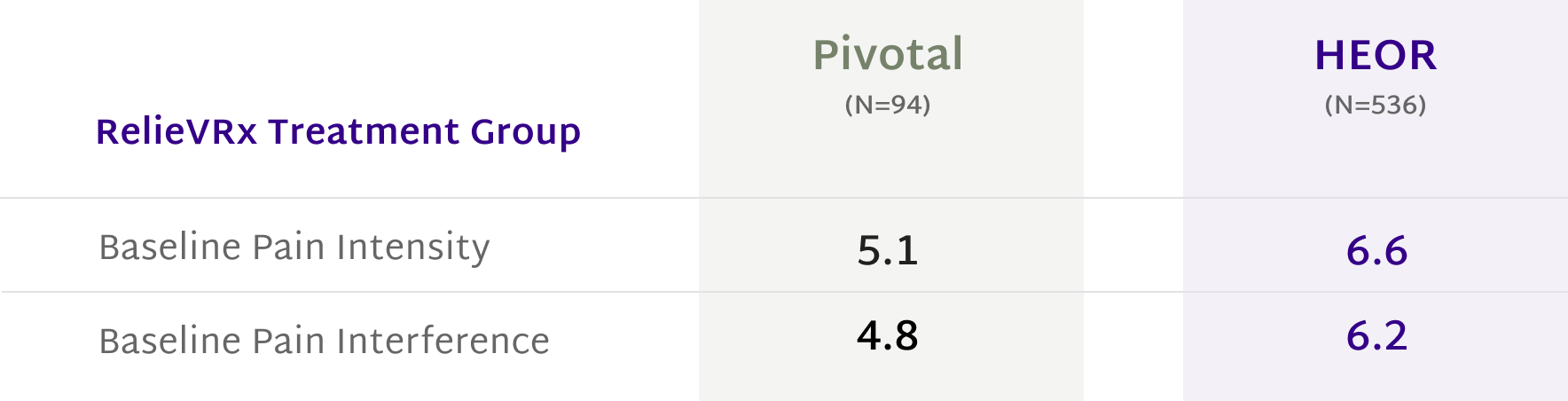
Rooted in Science, Proven in Practice
At the end of the 56-session program, those with moderate-to-severe CLBP experienced significant pain reduction compared with the Sham VR device.2,4
Give patients with CLBP the relief they need
People with CLBP typically take more medications than the average patient, which may include opioids5. Opioids can cause complications or side effects and are not an effective long term treatment for chronic lower back pain6. A comprehensive approach is needed to improve patient lives.
Learn how a new approach may help provide lasting relief, without the tradeoffs.
Contact us for updates about the RelieVRx program
If you are currently a RelieVRx patient and need assistance, please don't hesitate to call or email us
Indication for Use The RelieVRx program is a prescription-use immersive virtual reality system intended to provide adjunctive treatment based on cognitive behavioral therapy skills and other evidence-based behavioral methods for patients (age 18 and older) with a diagnosis of chronic lower back-pain (defined as moderate to severe pain lasting longer than three months). The device is intended for in-home use for the reduction of pain and pain interference associated with chronic lower back pain.
Contraindications
There are no known contraindications.
References
- “Device Classification under Section 513(F)(2)(De Novo).” https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfRL/rl.cfm?lid=764583&lpcd=QRA.
- Garcia LM, Birckhead BJ, Krishnamurthy P, et al. An 8-week self-administered at-home behavioral skills-based virtual reality program for chronic low back pain: double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial conducted during COVID-19. J Med Internet Res. 2021;23(2):e26292. doi:10.2196/26292
- Maddox T, Sparks C, Oldstone L, Maddox R, Ffrench K, Garcia H, Krishnamurthy P, Okhotin D, Garcia LM, Birckhead BJ, Sackman J, Mackey I, Louis R, Salmasi V, Oyao A, Darnall BD. Durable chronic low back pain reductions up to 24 months after treatment for an accessible, 8-week, in-home behavioral skills-based virtual reality program: a randomized controlled trial. Pain Med. 2023 Oct 3;24(10):1200-1203. doi: 10.1093/pm/pnad070. PMID: 37220894; PMCID: PMC10546478.
- Maddox, T., Oldstone, L., Sparks, C., Sackman, J., Oyao, A., Garcia, L., Maddox, R., Ffrench, K., Garcia, H., Irvin, A., Maislin, D., Keenan, B., Bonakdar, R., & Darnall, BD (2023). At-home virtual reality program for chronic lower back pain: A randomized sham-controlled effectiveness trial in a clinically severe and diverse sample. Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Digital Medicine, 2023;1(4):563-573.
- Gore M, Sadosky A, Stacey BR, Tai KS, Leslie D. The burden of chronic low back pain: clinical comorbidities, treatment patterns, and health care costs in usual care settings. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(11):E668-E677
- Deyo RA, Von Korff M, Duhrkoop D. Opioids for low back pain. BMJ. 2015;350:g6380.